Differentiated mathematics and morphogenetic processes
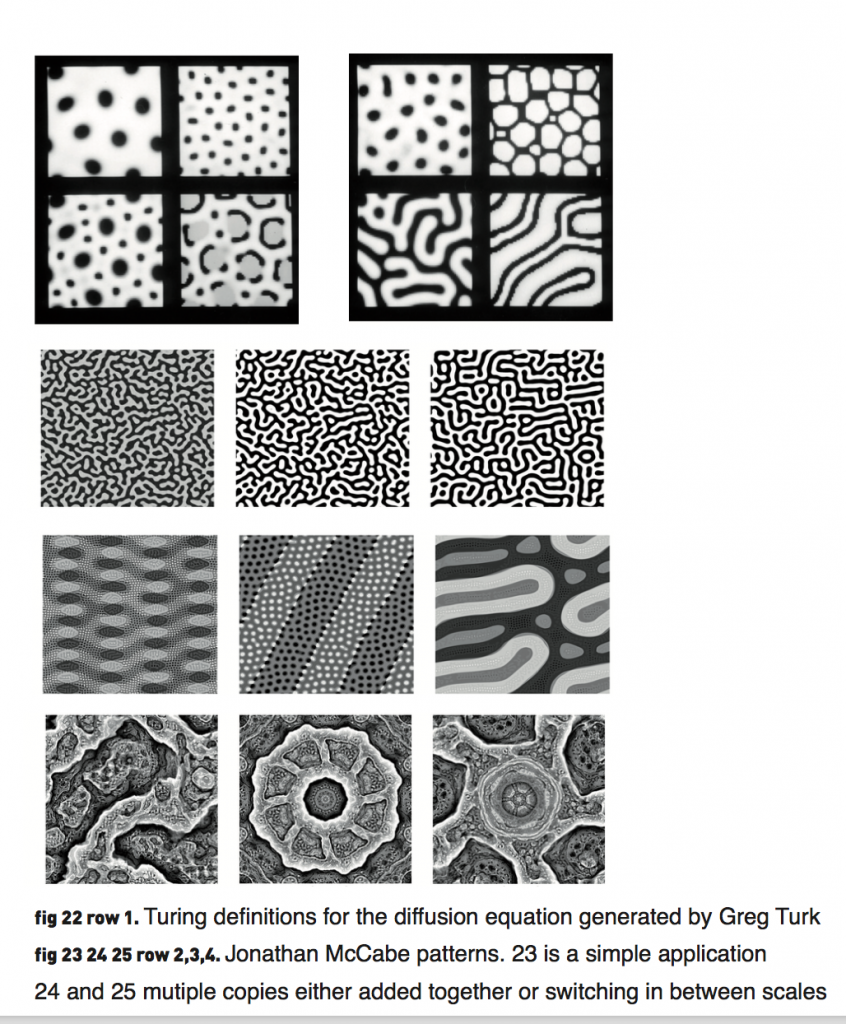
Alan Turing published a paper in 1952, The chemical basis of morphogenesis’ (ref 5). on the spontaneous formation of patterns in systems undergoing reaction and diffusion of their ingredients. Turing devised a mathematical model that explained how random fluctuations can drive the emergence of pattern and structure from initial uniformity.
Turing speculated that among the molecular ingredients of this bundle of cells are components called morphogens (‘shape-formers’), which are somehow responsible for triggering the development of a cell or tissue along a certain pathway. More specifically, a morphogen is a signalling molecule that acts directly on cells to produce specific cellular responses depending on its local concentration.
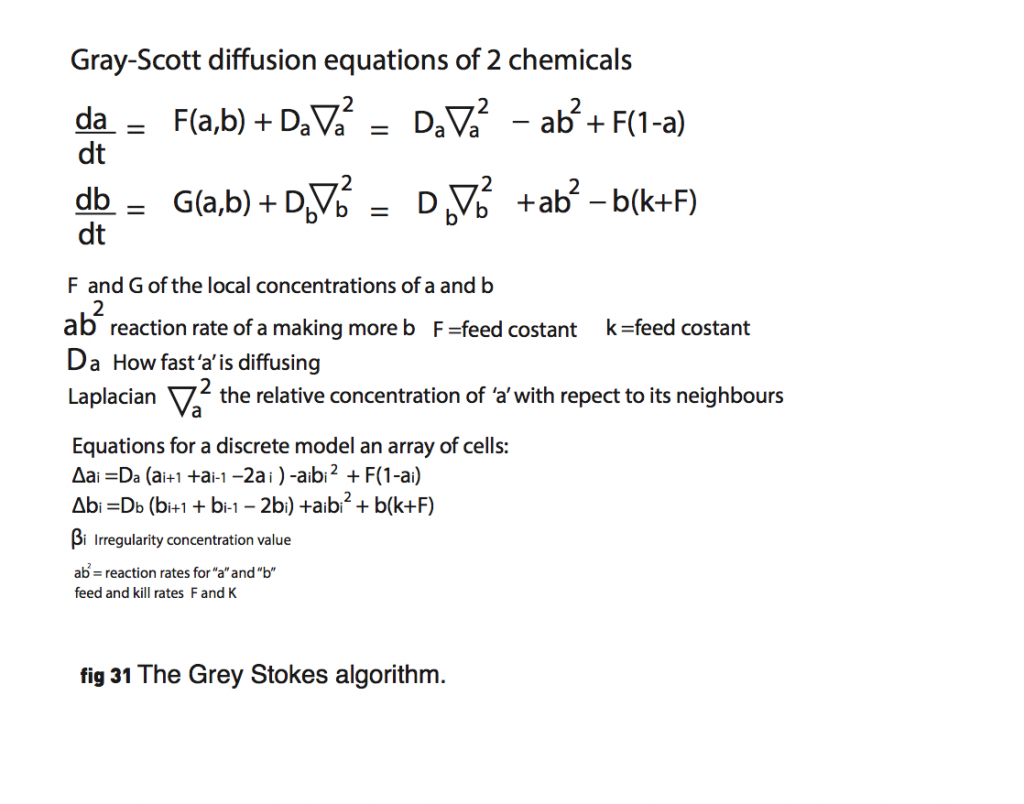
Turing diffusion equations of 2 chemicals:
My artefact consisted of a implemented interactive diffusion equation algorithm based on the Gray-Scott model (ref. 22). Figure 30. The user is able to dynamically control thealgorithm by clicking to add more “cells” and by dragging the mouse to change the feed parameter (F) and the kill parameter (k).
The Artefact
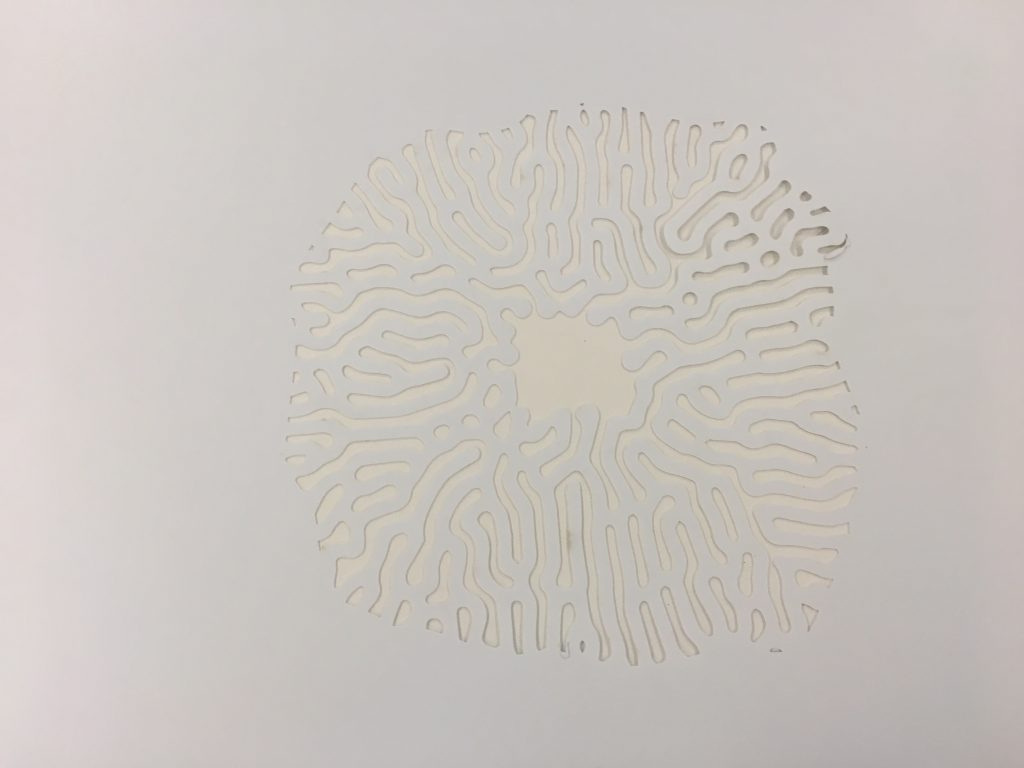
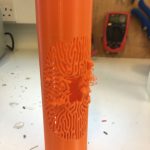
The software algorithm was run with a Gray-Scott algorithm. The results are shown below. The results show 2d outputs transferred into 3d models and output as prototypes. The idea here is to produce 4 large cylindrical ceramic lights ( approx 90cm height x 30cm diameter).
Clay Models